Demographics of Australia
|
|
Australia-demography.png
The demographics of Australia start with the arrival of Australia's indigenous people, a hunting-gathering people, the Australian Aborigines, who were estimated to have arrived between 50,000-60,000 years ago. Although their technical culture remained static—depending on wood, bone, and stone tools and weapons—their spiritual and social life was highly complex. Most spoke several languages, and confederacies sometimes linked widely scattered tribal groups. Aboriginal population density ranged from 1 person per square mile along the coasts to 1 person per 35 square miles in the arid interior. Food procurement was usually a matter for the nuclear family and was very demanding, since there was little large game, and outside of some communities in the fertile south-east, they had no agriculture.
Australia may have been sighted by Portuguese sailors in 1601, and Dutch navigators landed on the forbidding coast of modern Western Australia several times during the 17th century. Captain James Cook claimed it for Great Britain in 1770. At that time, the native population may have numbered 300,000 in as many as 500 tribes speaking many different languages. The Aboriginal population currently numbers more than 300,000, representing about 1.7% of the population. Since the end of World War II, efforts have been made both by the government and by the public to be more responsive to Aboriginal rights and needs.
Today, many tribal Aborigines lead a settled traditional life in remote areas of northern, central, and western Australia. In the south, where most Aborigines are of mixed descent, most live in the cities.
European arrivals
Main article: Australian immigration
Immigration has been a major factor in Australia's development since the beginning of European settlement in 1788. For generations, most settlers came from Britain and Ireland, and the people of Australia are still predominantly of British or Irish origin, with a culture and outlook similar to that of the United Kingdom and the United States.
Between 1839 and 1900 over 18,000 Germans came to Australia, especially the south; by 1890 they were the largest non-British section of the population. Some were persecuted Lutherans, others were economic or political refugees, for example the Forty-Eighters who fled Germany after the revolutions in 1848.
Since the end of World War II, the population has more than doubled; non-European immigration, mostly from the Middle East and Asia, has increased significantly since 1945 through an extensive, planned immigration program. From 1945 through 1996, nearly 5.5 million immigrants settled in Australia, and about 80% have remained; nearly one of every four Australians is foreign-born. Britain and Ireland have been the largest sources of post-war immigrants, followed by Italy, Greece, New Zealand, and the former Yugoslavia.
The 1970s saw progressive reductions in the size of the annual immigration program due to economic and employment conditions; in 1969-70, 185,000 persons were permitted to settle, but by 1975-76 the number had dropped to 52,700. Immigration has slowly risen since. In 1995-96, Australia accepted more than 99,000 regular immigrants. In 1999-2000, Australia accepted 82,000 new immigrants. In addition, since 1990 about 7,500 New Zealanders have settled in Australia each year.
- 1999-2000: 82,000
- 2000-2001: 107,336
- 2001-2002: 88,900
- 2002-2003: 93,914
- 2003-2004: 111,590
Settler Arrivals 1993-94 to 2003-04 (293KB, PDF) (http://www.immi.gov.au/statistics/publications/settler-arrivals/settarr-0304.pdf)
Current situation
Australian_population.PNG
Australia's refugee admissions of about 12,000 per year are in addition to the normal immigration program. In recent years, the government has given priority to refugees from the former Yugoslavia, the Middle East, and Africa. In recent years, refugees from Indochina and the former Yugoslavia have comprised the largest single element in Australia's refugee program.
Emigration now also plays a role in changing Australian demographics. The term, Australian Diaspora, refers to the 850,000 Australian citizens who today live outside Australia. This phenomenon is relatively new in Australia's history, estimated as having occurred over the last 40 years. Awareness of this demographic (almost 5% of the Australian population) is growing and supported by government initiates.
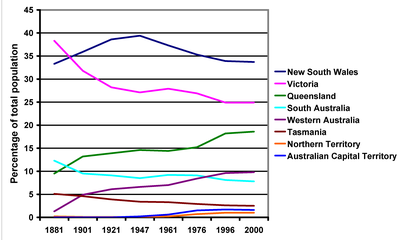
Although Australia has scarcely more than two persons per square kilometer of total land area, this raw figure is highly misleading: most of the continent is desert or semi-desert and of no agricultural value. In consequence, Australia is one of the world's most urbanized countries: less than 15% of the population live in rural areas.
Demographic data from the CIA World Factbook
Population
- 20,090,437 (July 2005 est.)
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 19.8% (male 2,038,809/female 1,943,563)
- 15-64 years: 67.2% (male 6,815,600/female 6,695,189)
- 65 years and over: 12.9% (male 1,145,274/female 1,452,002) (2005 est.)
Median age
- Total: 36.56 years
- Male: 35.74 years
- Female: 37.4 years (2005 est.)
Population growth rate
- 0.87% (2005 est.)
Birth rate
- 12.26 births/1,000 population (2005 est.)
Death rate
- 7.44 deaths/1,000 population (2005 est.)
Net migration rate
- 3.91 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2005 est.)
Sex ratio
- At birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
- Under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female
- Total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2005 est.)
Infant mortality rate
- Total: 4.69 deaths/1,000 live births
- Male: 5.08 deaths/1,000 live births
- Female: 4.27 deaths/1,000 live births (2005 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- Total population: 80.39 years
- Male: 77.52 years
- Female: 83.4 years (2005 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 1.76 children born/woman (2005 est.)
HIV/AIDS
- Adult prevalence rate: 0.1% (2003 est.)
- People living with HIV/AIDS: 14,000 (2003 est.)
- Deaths: less than 200 (2003 est.)
Nationality
- Noun: Australian(s)
- Adjective: Australian
Ethnic groups
- Caucasian 92%, Asian 7%, aboriginal and other 1%
Religions
- Anglican 26.1%, Roman Catholic 26%, other Christian 24.3%, non-Christian 11%, other 12.6%
Languages
- Official: English
- Most common languages other than English: Chinese languages, Italian, Greek, Arabic
- Indigenous: Australian Aboriginal languages, Australian Deaf Sign Language
Literacy
- Definition: age 15 and over can read and write
- Total population: 100%
- Male: 100%
- Female: 100% (1980 est.)