Fetal hemoglobin
|
|
Hemoglobin_F.png
Fetal hemoglobin (also hemoglobin F or HbF) is the main oxygen transport protein in the fetus during the last seven months of development in the womb. Functionally, fetal hemoglobin differs most from adult hemoglobin in that it is able to bind oxygen with greater affinity than the adult form, giving the developing fetus better access to oxygen from the mother's bloodstream. The reactivation of fetal hemoglobin synthesis in adults has been used as a viable treatment for sickle cell anemia since 1995.
| Contents |
Overview
HbA_vs_HbF_saturation_curve.png
Both mother and fetus share a common blood supply. In particular, the fetus's blood supply is delivered via the umbilical vein from the placenta, which is anchored to the wall of the mother's uterus. As blood courses through the mother, oxygen is delivered to capillary beds for gas exchange, and by the time blood reaches the capillaries of the placenta, its oxygen saturation has decreased considerably. In order to recover enough oxygen to sustain itself, the fetus must be able to bind oxygen with a greater affinity than the mother.
Fetal hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen is substantially greater than that of adult hemoglobin. Notably, the P50 value for fetal hemoglobin (i.e., the partial pressure of oxygen at which the protein is 50% saturated; lower values indicate greater affinity) is roughly 19 mmHg, whereas adult hemoglobin has a value of approximately 26.8 mmHg. As a result, the so-called "oxygen saturation curve", which plots percent saturation vs. pO2, is left-shifted for fetal hemoglobin in comparison to the same curve in adult hemoglobin.
Distribution
After the first 10 to 12 weeks of development, the fetus' primary form of hemoglobin switches from embryonic hemoglobin to fetal hemoglobin. At birth, fetal hemoglobin comprises 50-95% of the child's hemoglobin. These levels decline after six months as adult hemoglobin synthesis is activated while fetal hemoglobin synthesis is deactivated. Soon after, adult hemoglobin (hemoglobin A in particular) takes over as the predominant form of hemoglobin in normal children.
Structure and genetics
Most types of normal hemoglobin, including hemoglobin A, hemoglobin A2, hemoglobin S, and hemoglobin F, are tetramers composed of four protein subunits and four heme prosthetic groups. Whereas adult hemoglobin is composed of two alpha and two beta subunits, fetal hemoglobin is composed of two alpha and two gamma subunits, commonly denoted as α2γ2. Because of its presence in fetal hemoglobin, the gamma subunit is commonly called the "fetal" hemoglobin subunit.
In humans, each chromosome 11 contains two identical copies of the gene that encodes the gamma subunit. The gene that codes for the alpha subunit is located on chromosome 16 and is also present in duplicate.
Treatment of sickle cell anemia
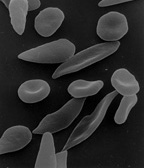
When fetal hemoglobin production is switched off after birth, normal children begin producing hemoglobin A. But children with sickle cell anemia instead begin producing a long, slender form of hemoglobin called hemoglobin S. This variety of hemoglobin causes red blood cells to change their shape from round to sickle-shaped, which have a greater tendency to stack on top of one another and crowd blood vessels. These invariably lead to so-called painful vaso-occlusive episodes, which are a hallmark of the disease.
If fetal hemoglobin remains the predominant form of hemoglobin after birth, however, the number of painful episodes decreases in patients with sickle cell anemia. Hydroxyurea, used also as an anti-cancer drug, is a viable treatment for sickle cell anemia, as it promotes the production of fetal hemoglobin while inhibiting sickling due to hemoglobin S polymerization.
Combination therapy with hydroxyurea and recombinant erythropoietin—rather than treatment with hydroxyurea alone—has been shown to further elevate hemoglobin F levels and to promote the development of HbF-containing F-cells [1] (http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/abstract/328/2/73).
References
- Hemoglobin synthesis (http://sickle.bwh.harvard.edu/hbsynthesis.html)
- Hemoglobin structure and function (http://ntri.tamuk.edu/homepage-ntri/lectures/protein/hemoglobin/hempage.html)
- Hemoglobin F fact sheet (http://www.fha.state.md.us/genetics/html/hemo_f.html)
- Fetal hemoglobin (http://www.isat.jmu.edu/users/klevicca/isat454/FetalHb.doc) [doc]
- Hydroxyurea in sickle-cell disease (http://sickle.bwh.harvard.edu/hyguid.html)
- Management of sickle-cell disease (http://www.scinfo.org/nihnewchap26.htm)
- Effect of hydroxyurea on the frequency of painful crises in sickle cell anemia (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=7715639) (original 1995 study)
External links
- Hemoglobinopathies (http://sickle.bwh.harvard.edu/hemoglobinopathy.html)
- Transport across the placenta (http://arbl.cvmbs.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/reprod/placenta/transport.html)
- American Sickle Cell Anemia Association (http://www.ascaa.org/ftreat.htm)
