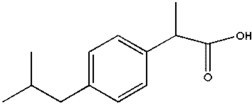
Ibuprofen
|
|
|
2-(p-isobutylphenyl)propionic acid | |
| Empirical formula | C13H18O2 |
| Molecular weight | 206.3 |
| Bioavailability (Oral) | unknown |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Half life | 1.9-2.2 hours |
| Excretion | renal |
| Pregnancy category | C (Australia) |
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve the symptoms of arthritis, primary dysmenorrhoea, fever; and as an analgesic, especially where there is an inflammatory component. Ibuprofen was developed by the research arm of Boots. It is widely marketed under various trademarks including Act-3, Advil, Brufen, Motrin, Nuprin, and Nurofen.
| Contents |
Indications
Approved clinical indications for ibuprofen include:
- rheumatoid arthritis
- osteoarthritis
- juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- primary dysmenorrhoea
- fever
- relief of acute and/or chronic pain states in which there is an inflammatory component
Ibuprofen is widely used for the relief of headache including migraine. It is also widely marketed as an analgesic agent (rather than as an anti-inflammatory) and is often used for general pain conditions including those that arise from various injuries (such as sporting injuries), illnesses (such as influenza, shingles, gout), and post-operative pain.
As with other NSAIDs, ibuprofen inhibits platelet aggregation, but is not used therapeutically for this action since it is a minor and reversible effect.
Mechanism of action
Ibuprofen is an NSAID and, as such, is believed to work through inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX); thus inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis.
Main article: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Adverse effects
Ibuprofen appears to have the lowest incidence of gastrointestinal adverse drug reactions (ADRs) of all the non-selective NSAIDs. However, this only holds true at lower doses of ibuprofen, so over-the-counter preparations of ibuprofen are generally labelled to advise a maximum daily dose of 1.2 grams.
Main article: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Reported ADRs
Common adverse effects include: nausea, dyspepsia, gastrointestinal ulceration/bleeding, raised liver enzymes, diarrhoea, headache, dizziness, salt and fluid retention, hypertension (Rossi, 2004).
Infrequent adverse effects include: oesophageal ulceration, heart failure, hyperkalaemia, renal impairment, confusion, bronchospasm, rash (Rossi, 2004)
Photosensitivity
As with other NSAIDs, ibuprofen has been reported to be a photosensitising agent. (Castell et al., 1987) Ibuprofen, however, has a very weak absorption spectrum which does not reach into the solar spectrum. The molecule contains only a single phenyl moiety, and no bond conjugation, resulting in a very weak chromophore system. Ibuprofen, therefore, is only a very weak photosensitising agent when compared with other members of the 2-arylpropionic acids.
Heart attack risk
Along with several other NSAIDs, ibuprofen has been implicated in elevating the risk of myocardial infarction, particularly among those chronically using high doses. (Hippisley-Cox, 2005)
Stereochemistry
Ibuprofen, like other 2-arylpropionate derivatives (including ketoprofen, flurbiprofen, naproxen, etc) contains a chiral carbon in the β-position of the propionate moiety. As such there are two possible enantiomers of ibuprofen with the potential for different biological effects and metabolism for each enantiomer.
Indeed it was found that S-ibuprofen (sinisteribuprofen) was the active form both in vitro and in vivo.
Logically then, there was the potential for improving the selectivity and potency of ibuprofen formulations by marketing ibuprofen as a single-enantiomer product (as occurs with naproxen, another NSAID).
Further in vivo testing, however, revealed the existence of an isomerase which converted R-ibuprofen to the active S-enantiomer. Thus, due to the expense and futility that might be involved in marketing the single-enantiomer, all ibuprofen formulations currently marketed are a racemic mixture of both enantiomers.
Availability
Ibuprofen was made available under prescription in the United Kingdom in 1969. In the years since, the good tolerability profile along with extensive experience in the community (otherwise known as Phase IV trials), has resulted in the rescheduling of small packs of ibuprofen to allow availability over-the-counter in pharmacies worldwide. Indeed there has been an increasing trend towards descheduling ibuprofen such that it is now available in supermarkets and other general retailers; in fact, in the United States, ibuprofen (most commonly in a 200mg dosage) is about as widely used as aspirin and acetaminophen as an over-the-counter painkiller.
References
- Rossi S (Ed.) (2004). Australian Medicines Handbook 2004. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook. ISBN 0-9578521-4-2.
- Castell JV, Gomez MJ, Miranda MA, Morera IM (1987). Photolytic degradation of ibuprofen. Toxicity of the isolated photoproducts on fibroblasts and erythrocytes. Photochem Photobiol 46 (6), 991-6.
- Hippisley-Cox J, Coupland C (2005). Risk of myocardial infarction in patients taking cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors or conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: population based nested case-control analysis. British Medical Journal 2005;330:1366 (11 June).
| Analgesics edit (https://academickids.com:443/encyclopedia/index.php?title=Template:Analgesics&action=edit) | ||
|---|---|---|
|
{Paracetamol (acetaminophen) } {Tetrahydrocannabinol} {Cannabinoids} {Ketamine} | ||
| ||
| ||
de:Ibuprofen fr:Ibuprofène ms:Ibuprofen nl:Ibuprofen pl:Ibuprofen ru:Ибупрофен sv:Ibuprofen