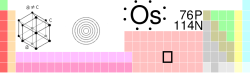
Osmium
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name, Symbol, Number | Osmium, Os, 76 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical series | transition metals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, Period, Block | 8 (VIIIB), 6, d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density, Hardness | 22610 kg/m3, 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Silvery, Blue Cast Missing image Os,76.jpg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic weight | 190.23 amu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius (calc.) | 130 (185) pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 128 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| van der Waals radius | no data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe]4f145d66s2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e- 's per energy level | 2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states (Oxide) | 4, 6, 8 (mildly acidic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | hexagonal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State of matter | Solid (__) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 3306 K (5491 ?F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 5285 K (9054 ?F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar volume | 8.42 ×10-6 m3/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 627.6 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 31.8 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | 2.52 Pa at 3300 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound | 4940 m/s at 293.15 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | 2.2 (Pauling scale) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specific heat capacity | 130 J/(kg*K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical conductivity | 10.9 106/m ohm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 87.6 W/(m*K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1st ionization potential | 840 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd ionization potential | 1600 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most stable isotopes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SI units & STP are used except where noted. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Osmium is a chemical element in the periodic table that has the symbol Os and atomic number 76. A hard brittle blue-gray or blue-black transition metal in the platinum family, osmium is the densest natural element and is used in some alloys with platinum and iridium. Osmium is found native as an alloy in platinum ore and its tetroxide has been used to stain tissues and in fingerprinting. Alloys of osmium are employed in fountain pen tips, electrical contacts and in other applications where extreme durability and hardness are needed.
| Contents |
Notable characteristics
Osmium in a metallic form is extremely dense, blue white, brittle and lustrous even at high temperatures, but proves to be extremely difficult to make. Powdered osmium is easier to make, but powdered osmium exposed to air leads to the formation of osmium tetroxide (OsO4), which is toxic. The oxide is also a powerful oxidizing agent, emits a strong smell and boils at 130?C.
Due to its very high density osmium is generally considered to be the heaviest known element, narrowly defeating iridium. However, calculations of density from the space lattice may produce more reliable data for these elements than actual measurements and give a density of 22650 kg/m3 for iridium versus 22610 kg/m3 for osmium. Definitive selection between the two is therefore not possible at this time. If one distinguishes different isotopes, then the heaviest ordinary substance would be Osmium-192.
This metal has the highest melting point and the lowest vapor pressure of the platinum family. Common oxidation states of osmium are +4 and +3, but oxidation states from +1 to +8 are observed.
Applications
Because of the extreme toxicity of its oxide, osmium is rarely used in its pure state, and is instead often alloyed with other metals that are used in high wear applications. Osmium alloys are very hard and along with other platinum group metals is almost entirely used in alloys employed in the tips of fountain pens, phonograph needles, instrument pivots, and electrical contacts.
Osmium tetroxide has been used in fingerprint detection and in staining fatty tissue for microscope slides. An alloy of 90% platinum and 10% osmium (90/10) is used in surgical implants such as pacemakers and replacement pulmonary valves.
The tetroxide (and a related compound, potassium osmate) are important oxidants for chemical synthesis.
History
Osmium (Greek osme meaning "a smell") was discovered in 1803 by Smithson Tennant in London, England along with iridium in the residue of dissolving platinum in aqua regia.
Occurrence
This transition metal is found in iridiosmium a naturally occurring alloy of iridium and osmium and in platinum-bearing river sands in the Ural Mountains, and North and South America. It is also occurs in nickel-bearing ores found in the Sudbury, Ontario region with other platinum group metals. Even though the quantity of platinum metals found in these ores is small, the large volume of nickel ores processed makes commercial recovery possible.
Compounds
Osmium tetroxide OsO4
Isotopes
Osmium has seven naturally-occurring isotopes, 5 of which are stable: Os-187, Os-188, Os-189, Os-190, and (most abundant) Os-192. Os-184, Os-186 have absurdly long half lifes and for practical purposes can be considered to be stable as well. Os-187 is the daughter of rhenium-187 (half-life 4.56 x 1010 years) and is most often measured in a Os-187/Os-188 ratio. This ratio, as well as the Re-187/Os-187 ratio, have been used extensively in dating terrestrial as well as meteoric rocks. However, the most notable application of Os in dating has been in conjunction with iridium, to analyze the layer of shocked quartz along the K-T boundary that marks the extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago.
Precautions
Osmium tetroxide is highly toxic. Airborne concentrations of osmium as low as 10-7 g/m? can cause lung congestion, skin or eye damage.
References
- Los Alamos National Laboratory - Osmium (http://periodic.lanl.gov/elements/76.html)
External links
- WebElements.com - Osmium (http://www.webelements.com/webelements/elements/text/Os/index.html)
- EnvironmentalChemistry.com - Osmium (http://environmentalchemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Os.html)