Romania
|
|
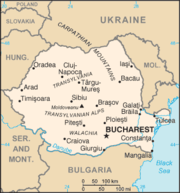
Romania (formerly spelled Rumania or Roumania; Romanian: Rom⮩a) is a country in southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Ukraine and Moldova in the northeast; Hungary in the west; Serbia and Bulgaria to the south along the Danube River. Romania has a stretch of sea coast on the Black Sea and the eastern and southern Carpathians mountains run through its center.
| |||||
| Motto: none former Royal motto: "Nihil Sine Deo" (Nothing without God) | |||||
| Anthem: Deşteaptă-te, Rom⮥! | |||||

| |||||
| Capital | Bucharest Template:Coor dm | ||||
| Largest city | Bucharest | ||||
| Official languages | Romanian | ||||
| Government | Democratic republic Traian Băsescu Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu | ||||
| Independence - Declared - Recognised | Romanian War of Independence 10 May, 1877 13 July, 1878 (Treaty of Berlin) | ||||
| Area • Total • Water (%) | 238,319 km² (78th) 3% | ||||
| Population • 2004 est. • 2002 census • Density | 22,355,551 (49th) 21,698,181 91.3/km² (102nd) | ||||
| GDP (PPP) • Total • Per capita | 2004 estimate 183.162 billion USD (46th) 8,258 USD (70th) | ||||
| Currency | Leu (ROL)
| ||||
| Time zone • Summer (DST) | EET (UTC+2) EEST (UTC+3) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .ro | ||||
| Calling code | +40
| ||||
| Contents |
Name
Main article: Etymology of Romania
The name of Romania (Rom⮩a) comes from Rom⮧' (which means "Romanian" in the Romanian language, being a derivate of the word "Roman" from Latin). Also, "Ţara Rom⮥ască" (The Romanian Country) is the Romanian name of the former principality of Wallachia.
History
Main article: History of Romania
In 513 BC, on what is now the country of Romania, the tribal confederation of the Getae were encountered by Darius during his campaign in the Balkans. The Dacians resisted Darius, but were later defeated by the Roman Empire under Emperor Trajan in two campaigns stretching from 101 to 106, and the core of their kingdom was turned into the Roman province of Dacia. The Gothic and Carpic campaigns in the Balkans during 238–256 forced the Roman Empire to reorganize a new Roman province of Dacia south of Danube, inside former Moesia Superior. In 271 the ancient Dacia became the Kingdom of the Goths until the end of the fourth century, when it was included in the Hunnic Empire. The Gepids and the Avars ruled Transylvania until eighth century, thence the Bulgars included Romania in their Empire until 1000. The Pechenegs, the Cumans and Uzes were also mentioned by historic chronicles on the territory of Romania until the founding of the Valachian principalities of Wallachia by Basarab I, and Moldavia by Dragos during the 13th and 14th century respectively. In the Middle Ages, Romanians lived in three distinct principalities: Walachia, Moldavia, and Transylvania.
Wallachia and Moldavia came under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire during 15th and 16th century respectively, with internal autonomy under the millet system, and brief periods of independence. Moldavia lost its eastern side Bessarabia to the Russian Empire in 1812 (though partially regained it with the Treaty of Paris in 1856), its northern part Bukovina to the Austrian Empire in 1775 and its south-eastern part Bugeac to the Ottoman Empire.
Transylvania came under control of the Kingdom of Hungary by 12th century (since 1301 Hungary and Transylvania became possessions of House of Anjou, of Habsburg, and of Holy Roman Empire). Later, in 1526, it became a Principality under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire, following the Battle of Mohacs. At the end of the 18th century, the Austrian Empire (since 1867 Austria-Hungary) incorporated Transylvania until 1918 at the end of World War I.
The modern state of Romania was formed by the merging of the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia in 1859 under the domnitor Alexandru Ioan Cuza. He was replaced by a Hohenzollern dynasty in 1866, and independence and status as a kingdom were recognised by the Great Powers in 1878, following the Russo-Turkish War, in which Romania fought on the Russian side. At that time, Russia once again seized the two districts of Bessarabia that had been regained by Moldova after the Crimean War 1852, as a swap with Dobrudja. At the end of the World War I, which brought the disintegration of the empires of Russia and Austro-Hungary and the rise of Bolshevism in Hungary and Russia, Bessarabia and Transylvania united with the Romanian Kingdom in 1918. Union of Tranylvania with Romania was ratified in the Treaty of Trianon in 1920.
In 1940, at the beginning of World War II, northern Bukovina and Bessarabia, Northern Transylvania, and southern Dobrudja were occupied by the Soviet Union, Hungary and Bulgaria respectively, Romania being under the dictatorship of Carol II. In 1940 Carol II abdicated and Romania entered the war joining Germany, Hungary and Bulgaria, thus recovering Bessarabia and northern Bukovina from the Soviet Union and taking part in the ensuing invasion, under the lead of general Antonescu. In August 1944 the Antonescu regime was toppled, Romania joined the Red Army against Nazi Germany, but its role in the defeat of Germany was not recognised by the 1946 Treaty of Paris. In 1947, King Michael I was forced by the communists to abdicate and leave the country, and Romania became a communist state, under direct military and economic control of the USSR until 1958.
The decades-long reign of Communism under Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej, then under Nicolae Ceauşescu, ended in late 1989 (see Romanian Revolution of 1989), and the elections of 1990 were won by FSN, part of which, reformed as the Social Democrats, continued to be present in the democratically elected government until 1996 when CDR, a center-right coalition took power for one term. After repudiating their 'Contract With Romania' platform which would have required the CDR to resign en masse after 200 days from a mixed coalition government (some members had signed on to the contract program while others had not), the major CDR parties were electorally eviscerated in 2000, and the Social Democrats returned to power.
The leader of the Democratic Party, Traian Băsescu was elected President on December 12, 2004, and took office December 20. Traian Băsescu managed to form a government around his own political party, the Truth and Justice Alliance (Alianta Dreptate si Adevar), by appointing Prime Minister Calin Popescu Tariceanu. The Alliance formed a government with the Romanian Humanist Party (Partidul Umanist Roman) now the Conservative Party, which was formerly allied to the Social Democrats, but switched sides, and an ethnic minority rights party, the Democratic Alliance of Hungarians in Romania (Uniunea Democrata a Maghiarilor din Romania), which has participated in government since 1996.
Following the end of the Cold War in 1989, Romania developed closer ties with Western Europe, joined NATO in 2004 and became an acceding country to the European Union, hoping to join on January 1, 2007.
See also: Kings of Romania, Bessarabia, Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania
Politics
Main article: Politics of Romania
Romania is a democratic republic. The legislative branch of the Romanian government consists of two chambers, the Senat (Senate), which has 137 members (as of 2004), and the Camera Deputaţilor (Chamber of Deputies), which has 332 members (as of 2004). The members of both chambers are chosen in elections held every four years.
The President, the head of the executive branch, is also elected by popular vote, every five years (until 2005, four years). The president appoints a prime minister, who heads the government, the members of which are in turn appointed by the prime minister. The government is subject to a parliamentary vote of approval.
Counties
Main article: Counties of Romania
Romania is divided into 41 judeţe, or counties, and the municipality of Bucharest (Bucureşti) - the capital.
The counties are (in alphabetical order):

Transylvania is green, Wallachia blue, the Moldavian region red, and Dobrogea yellow
Geography
Main article: Geography of Romania
A large part of Romania's borders with Serbia and Bulgaria is formed by the Danube. The Danube is joined by the Prut River, which forms the border with Moldova. The Danube flows into the Black Sea forming the Danube Delta which is a reservation of the Biosphere.
The Carpathian Mountains dominate the center of Romania surrounding the Transylvanian Plateau, with peaks up to 2,500 m, the highest, Moldoveanu, reaching 2,544 m. In the south, the Carpathians sweeten into hills, towards the B㲣gan plains.
Major cities are the capital Bucharest, Braşov, Timişoara, Cluj-Napoca, Constanţa, Craiova, Iaşi and Galati.
See also:
Economy
Main article: Economy of Romania
After Romania's Communist regime was overthrown in late 1989, the country was left with an obsolete industrial base and a pattern of industrial capacity wholly unsuited to its needs. This led to the country experiencing several years of recession in the early 1990s.
In February 1997, Romania embarked on a comprehensive macroeconomic stabilisation and structural reform programme, but reform remained a frustrating stop-and-go process until 2000, when Romania started negotiations with the European Union and reforms were accelerated, even though deep reforms were only begun in 2004. Restructuring programs include liquidating large energy-intensive industries and major agricultural and financial sector reforms.
Romania's lagging and unstable economy of the 1990s has been transformed into one with macroeconomic stability, high growth and low unemployment, although a high inflation rate of 9.2% (as of 2004) remains a problem. 2002 and 2003 were successful economic years, and currently GDP growth is forecast at 5.5% per annum. The economy grew by 8.3% in 2004, the fastest growth in the post-Communist era. Foreign direct investments reached EUR 4.1 billion in 2004. Romania was granted in October 2004 the much desired 'functional market economy' status by EU officials, and is expected to join the EU in January 2007.
In January 2005, Romania's new Tăriceanu government imposed major fiscal reforms, replacing Romania's progressive tax system with a 16% flat tax on both personal income and company profit. Romania now has one of the most liberal taxation systems in Europe, and this, along with increased foreign investment, is expected to boost economic growth in the coming years, as well as lower corruption and bring to light the grey economy.
The average gross wage per month in Romania is 972.98 new lei as of April 2005, an increase of 5.7% over the previous month. This equates to 268.87 euro, US$328.76. The average net salary per month in April 2005 was 743.48 new lei (205.46 euro), an increase of 5.0%, over the previous month.
Unemployment in Romania is at 5.7% (April 2005), which is very low compared to other large European countries such as Poland, France, or Germany.
Despite the improvements in macroeconomics, privatisation and fiscal policy of the last few years, corruption remains a major problem at all levels and threatens to stifle economic growth. Additionally, lack of transparency in public spending and lack of competitiveness in the agricultural sector remain problems.
Romania's legal tender is the leu (plural lei). On 1 July 2005, the leu will be subject to redenomination so that 10,000 old lei, in circulation on that date, shall be exchanged for 1 new leu. The existing banknotes and coins, i.e. the old lei, will be legal tender until the end of December 2006. By 31 December 2006, the existing banknotes and coins, i.e. the old lei, are to be replaced gradually by the new banknotes and coins. The ISO code for the old currency, ROL (Romanian Leu) will be replaced with RON (Romanian New). The process will prepare Romania for the adoption of the euro, which is expected to take place several years after EU accession. The Romanian government has said that it expects the country will adopt the euro between 2012 and 2014.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Romania
Ethnicity
Ethnic groups (Census 2002):
- Romanian 89.5%
- Hungarian 6.6%
- Rroma (Gypsy) 2.47%
- Ukrainian 0.3%
- German 0.3%
- Russian 0.2%
- Turkish and Tatar 0.2%
- Other 0.4%
The official language is Romanian, a Romance language of the Italic subfamily of the Indo-European family of languages, which are also called Romanic or Romantic languages. This language family includes French, Spanish, Italian and Portuguese; its languages are spoken by about 670 million people in many parts of the world, but mainly in Europe and the Western Hemisphere.
Sizeable minorities of Hungarian and German descent, mostly in Transylvania, also speak Hungarian and German. Other ethnic groups include Rroma and natives of Romania's neighbouring countries. There are also some other like Polish minority (numbering a few thousand people) living in Suceava County.
Some people say that the Rroma population is undercounted in national censuses (by this account, some Rroma choose to declare themselves as Romanians or Hungarians). The Rroma people are commonly known in Romania as ţigani (tzigany).
Religion
Religions (2002 est.):
- Romanian Orthodox - 86.7%
- Roman Catholic - 4.7%
- Protestant - 3.7%
- Pentecostal - 1.5%
- Greek Catholic - Uniate - 0.9%
Most Romanians are members of the Romanian Orthodox Church, which is one of the churches of Eastern Orthodox Christianity. Catholicism (both Roman Catholic and Greek Catholic) and Protestantism are also represented, mostly in the areas inhabited by population closer to western influence.
In Dobrogea, the region lying on the shore of the Black Sea, there is a small Muslim minority (of Turkish and Tatar ethnicity), a remnant of the Ottoman rule and migrations from Crimea, respectively.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Romania
See also:
- List of Romanians
- Romanian-American
- Romanian poets
- Music of Romania
- Literature of Romania
- Art of Romania
- Christmas customs in Romania
- Tourism in Romania
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Romania
- Transportation in Romania
- Military of Romania
- Foreign relations of Romania
- List of Romania-related topics
- Holidays in Romania
- List of national parks of Romania
- Health Care in Romania
- History of Romania
External links
Official links
- Official site of the Romanian government (http://www.gov.ro/engleza/)
- Presidency of Romania (http://www.presidency.ro/?lang=en)
- The Romanian Senate (http://www.senat.ro/)
- Camera Deputaţilor (http://www.cdep.ro/pls/dic/site.page?id=103&idl=2) (lower house of Parliament)
- Tourism Ministry (http://www.mtromania.ro/page.html?lg=eng)
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs (http://www.mae.ro/index.php?lang=en)
Travel guides
- The Spirit of Romania - travel journals, photography, stories (http://www.spirit.ro/)
- Romania travel guide at Wikitravel (http://wikitravel.org/en/article/Romania)
- - Sibiu/Hermanstadt, European Cultural Capital in 2007 (http://www.sibiu2007.ro)
Historical Links
- Original Text Documents and Monument Information (http://www.patzinakia.ro/) on Romanian Medieval Ages at the Romanian Group for an Alternative History Website
Currency
- Romania Banknotes (http://numismondo.com/pm/rom/) - 1877 to current issues
- Exchange Rates (http://www.bnro.ro/En/Info/curs_ext.asp) - from the National Bank of Romania
- Information about redenomination (http://www.denominare.ro/common/htmls/en.htm)
| European Union (EU) and candidates for enlargement | Missing image European_flag.png Flag of the European Union |
|---|---|
|
Member countries: Austria | Belgium | Cyprus | Czech Republic | Denmark | Estonia | Finland | France | Germany | Greece | Hungary | Ireland | Italy | Latvia | Lithuania | Luxembourg | Malta | Netherlands | Poland | Portugal | Slovakia | Slovenia | Spain | Sweden | United Kingdom | |
|
Acceding countries joining on January 1, 2007: Bulgaria | Romania | |
| Countries in Europe |
|---|
| Albania | Andorra | Austria | Azerbaijan1 | Belarus | Belgium | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Bulgaria | Croatia | Cyprus2 | Czech Republic | Denmark | Estonia | Finland | France | Germany | Greece | Hungary | Iceland | Ireland | Italy | Latvia | Liechtenstein | Lithuania | Luxembourg | Macedonia | Malta | Moldova | Monaco | Netherlands | Norway | Poland | Portugal | Romania | Russia1 | San Marino | Serbia and Montenegro | Slovakia | Slovenia | Spain | Sweden | Switzerland | Turkey1 | Ukraine | United Kingdom | Vatican City |
| Dependencies: Akrotiri and Dhekelia2 | Faroe Islands | Gibraltar | Guernsey | Jan Mayen | Jersey | Isle of Man | Svalbard |
| 1. Country partly in Asia. 2. Usually assigned to Asia geographically, but often considered European for cultural and historical reasons. |